In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity expertise is in high demand. If you’re considering a career safeguarding data, networks, and systems from digital threats, pursuing cybersecurity engineering may be an excellent path forward.
This overview covers what cyber security engineers do day-to-day, the skills required, the steps to take, and tips for getting hired.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Education | Bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology or a related field. Master’s degree preferred. Relevant certifications like CISSP. |
| Salary | $99,730 average annual salary in the US (according to Bureau of Labor Statistics). Experienced professionals can earn over $120,000. |
| Work Environment | Primarily office-based, working on computers and technical security systems. May sometimes visit facilities to assess security onsite. |
| Main Role | Identify and mitigate security vulnerabilities in IT systems and networks. Implement security controls and measures. Respond to cyber incidents. Advise organization on security best practices. |
Learn – How To Become a cyber security insurance agent
Table of Contents
What Does a Cyber Security Engineer Do?
Cyber security engineers are professionals who design, develop, and implement security measures to protect an organization’s computer systems, networks, and sensitive information from unauthorized access or cyber-attacks. Their primary duties include:
- Performing security audits to identify vulnerabilities in networks, applications, operating systems, or hardware. They use penetration testing, risk assessments, and other methods to locate weak points.
- Developing security standards, policies, and procedures to improve defenses based on audit findings and analysis of attempted or successful breaches. This can cover email security, endpoint protection, network access controls, and more.
- Configuring and maintaining various security tools such as firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption technologies. They ensure tools are kept current and monitor for suspicious activity.
- Responding swiftly when cyber security incidents occur to determine how attackers gained access, limit damage, and implement solutions to prevent future recurrence.
- Proactively researching the latest security threats, hacking techniques, and best practices in cyber defense. Knowledge must be continually expanded in this rapidly evolving field.
- Collaborating across IT teams and departments to bake security into all systems and processes. Security should be considered from initial design through implementation and beyond.
In summary, cyber security engineers have an analytical, problem-solving mindset. Like hackers, they think creatively about breaking into systems – but they use that knowledge to reinforce defenses rather than exploit them.
What is the Work Environment Like?
The majority of cyber security engineers work full-time in office environments. With remote work on the rise, more opportunities to telecommute are emerging. You’ll collaborate regularly with security analysts, software developers, network engineers, CIOs, and department leaders across organizations.
The stakes are substantial when tasked with safeguarding sensitive data, computer systems and operations. High-pressure situations can arise, but successfully protecting your employer from major cyber attacks is extremely rewarding. Adaptability and levelheaded critical thinking are vital when responding to security incidents.
What Technical Skills Are Required?
To succeed in cyber security engineering, you’ll need proficiency across several technical domains:
- Networking – An in-depth understanding of network protocols, infrastructure, topology, and vulnerabilities is crucial. You must know how data travels across networks and where risks arise.
- Operating systems – Extensive knowledge of operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS is needed to identify and address OS-specific security issues.
- Programming – Scripting skills in languages like Python, Java, C++, Go, and Bash allow automation of security tasks like threat detection, log analysis, and more.
- Analytical thinking – Apply logical analysis and critical thinking across every aspect of the role, from spotting vulnerabilities to debugging complex issues.
- Communication skills – Clearly explain technical security concepts and solutions to both technical and non-technical audiences across the organization.
Steps to Starting a Cyber Security Engineering Career
If you’re interested in embarking on this career path, here are typical steps:
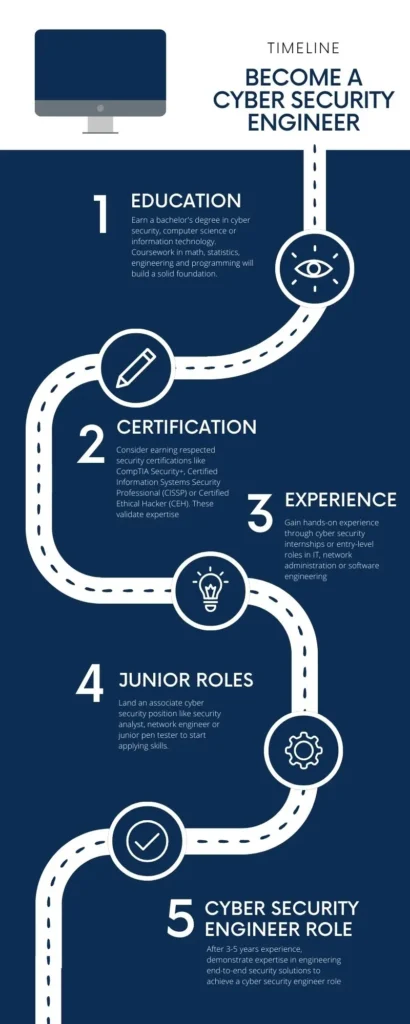
- Earn a bachelor’s degree in cyber security, computer science, or information technology. Coursework in math, statistics, engineering, and programming will build a solid foundation.
- Consider earning respected security certifications like CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH). These validate expertise.
- Gain hands-on experience through cyber security internships or entry-level roles in IT, network administration, or software engineering.
- Land an associate cyber security position like security analyst, network engineer, or junior pen tester to start applying skills.
- Continue expanding your technical skills and industry knowledge. Cybersecurity evolves rapidly, so lifelong learning is imperative.
- After 3-5 years of experience, demonstrate expertise in engineering end-to-end security solutions to achieve a cyber security engineer role.
Best Courses To Become A Cyber Security Engineer
- CompTIA Security+
- Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Security
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
What Should You Focus on in Job Interviews?
When interviewing, be prepared to:
- Discuss the latest cyber threats like ransomware, DDoS attacks, data breaches, and phishing. Explain associated risks and prevention methods.
- Communicate your understanding of core security concepts like encryption, VPNs, firewalls, multi-factor authentication, and more.
- Answer both technical questions on tools and approaches as well as behavioral questions on soft skills like communication, collaboration, and critical thinking.
- Ask thoughtful, researched questions showing your interest in the company’s security needs and enthusiasm for the potential role.
- Use specific examples of projects or experiences that prove you can architect innovative security solutions yourself.
- Exhibit professionalism, positivity about the field, and passion for security. Cyber security engineers need sharp yet personable team players.
What Should Your Resume Include?
When building your resume, be sure to:
- List any professional security certifications prominently. CISSP, CEH, and other credentials will grab attention.
- Feature your expertise across operating systems, networking, programming languages and security tools. Provide specifics.
- Highlight projects demonstrating security analysis skills like vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, threat modeling, etc. Quantify achievements.
- Incorporate relevant keywords like risk management, vulnerability assessment, SIEM, encryption, VPNs, firewalls and more.
- Use powerful action verbs like engineered, developed, detected, analyzed, mitigated, identified, etc.
- Structure your resume clearly and consistently with bullet points, ample white space, and no errors.
Launching a Cyber Security Engineering Career
Ready to help organizations defend against digital threats? With technical expertise, communication skills, and a passion for tackling challenges, you can embark on an exciting and meaningful career in cybersecurity engineering.
Identify open roles, refine your resume and interview abilities, and you could soon be applying your skills to protect our increasingly connected world.