Cyber threats are growing more sophisticated by the day, with phishing, ransomware, and hacking attacks becoming increasingly common. As a result, demand has exploded for cybersecurity professionals who can help organizations defend themselves.
If you enjoy combining problem-solving skills with cutting-edge technology, a career as a cybersecurity consultant could be very rewarding.
Let’s take a closer look at what these consultants do day-to-day and what it takes to break into the field. Let’s dig in.
Table of Contents
Who is a Cybersecurity Consultant
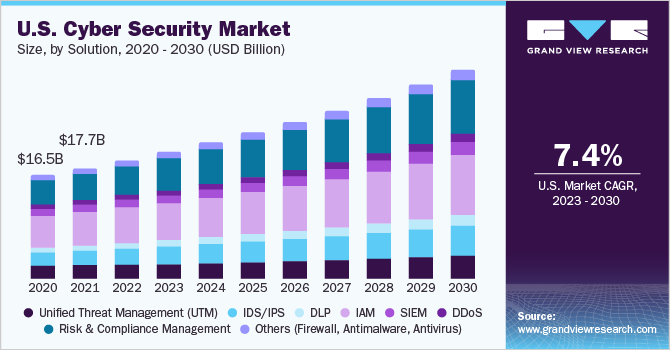
Cybersecurity is one of the economy’s fastest-growing sectors. As per GVR, The industry is projected to expand at a compound annual rate of over 7% through 2025 as threats multiply and businesses ramp up security budgets.
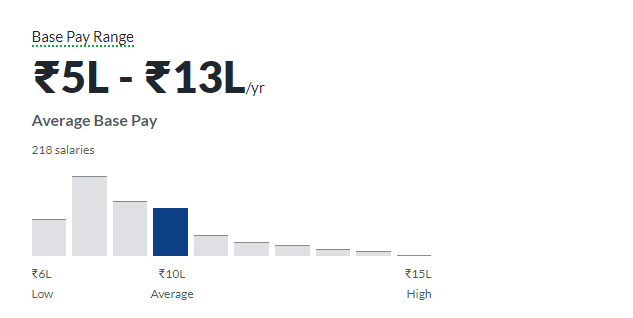
As a consultant, you help organizations assess vulnerabilities, implement solutions, and train employees on best practices. As per Glassdoor Median pay reaches nearly ₹13 lakh annually, with top consultants earning far more.
The work is challenging but gives you the chance to play a pivotal role in protecting high-profile clients.
Daily Responsibilities
As a cybersecurity consultant, you undertake a wide range of risk prevention, detection, and response initiatives. Core duties include:
- Conducting penetration tests to probe networks and applications for weaknesses
- Performing risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and quantify potential impacts
- Designing and implementing customized security solutions encompassing technology, policies, and employee training
- Educating clients on emerging cyber threats and security best practices
- Helping clients respond to and recover from breaches or incidents
- Staying on top of the latest trends in hacking techniques, malware, regulatory requirements, and more
Learn How To Become A Penetration Tester
Must-Have Skills
Mastering the technical side of cybersecurity is crucial yet not sufficient alone. You also need business acumen plus communication and teaching abilities. Key skills include:
1) Technical
- In-depth knowledge of threats like phishing, network intrusions, social engineering and mitigation techniques
- Ability to perform penetration testing, scanning networks and applications methodically for flaws
- Fluency in programming languages like Python and JavaScript
- Understanding of encryption protocols and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
2) Business
- Quantifying risks and prioritizing remediation based on potential business impact
- Articulating cybersecurity concepts and recommended solutions to non-technical stakeholders
- Project management principles for executing on complex initiatives spanning people, process, and technology
3) Interpersonal
- Presentation abilities to train employees on secure practices through engaging sessions
- Writing skills to produce clear reports synthesizing complex technical findings and recommendations
- Emotional intelligence to work collaboratively across an organization and build consensus
Career Pathways
You can pursue cybersecurity consulting through different avenues. Common trajectories include:
- Majoring in computer science or a similar technical discipline, then gaining 1-3 years of experience in IT security before moving into an advisory role
- Transitioning from another field like management consulting or auditing, leveraging transferrable skills
- Obtaining highly-valued certifications like the CISSP after being in IT and self-studying cybersecurity extensively
Once ready to become a consultant, you might work for a large IT services company, join a boutique cybersecurity firm, or even start your practice. And you can specialize in domains like healthcare, finance, or manufacturing.
Continuing Your Education
Given the dynamic, ever-evolving nature of cyber threats, ongoing learning is imperative for continued success as a consultant. Investing in skills sharpening and certifications also enables you to command higher fees.
Here are some of the most prestigious and valuable cybersecurity accreditations:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- GIAC Security Essentials Certification (GSEC)
- IAPSC Certified Security Consultant (CSC)
Whether taking a course focused on advanced persistent threats or gaining hands-on experience exploiting networks, learning is a lifelong habit.
Conclusion
So in summary, cybersecurity consulting offers dynamic work protecting prominent institutions from existential threats at the frontier of technology. It’s a prime option for those eager to plunge into an essential, fast-moving field almost guaranteed to expand for decades to come.
1 comment
Great content! This is exactly the sort of thing I was looking for. Thanks for your help 🙂